Android App¶
Languages¶
This page can be read in the following languages:
Objective¶
The objective of this tutorial is to create your first Android App integrating Beeping technology.
To do this we will follow the following steps:
-
A Beep creation
-
Creating an Android project
-
Android SDK installation
-
Using the Android SDK
-
Use a device to capture the content of the beep
Download the SDK¶
Here are the steps you must follow to create your first App.
The first thing we should do is download the Android SDK.
Click here to download the framework
Once downloaded we unzip it and leave the AndroidBeepingCore-release.aar file accessible for later.
Beep Creation¶
To create the beep follow the steps in the previous tutorial.
Click here to access the creation of your first beep
Once we have created the Beep we will have a file called ultrasound.wav with the content qa020. We leave the file accessible to play later.
App creation¶
Next we create our Android application.
We are going to use Android Studio.
Let's call our beeping-hello application.
Framework Installation¶
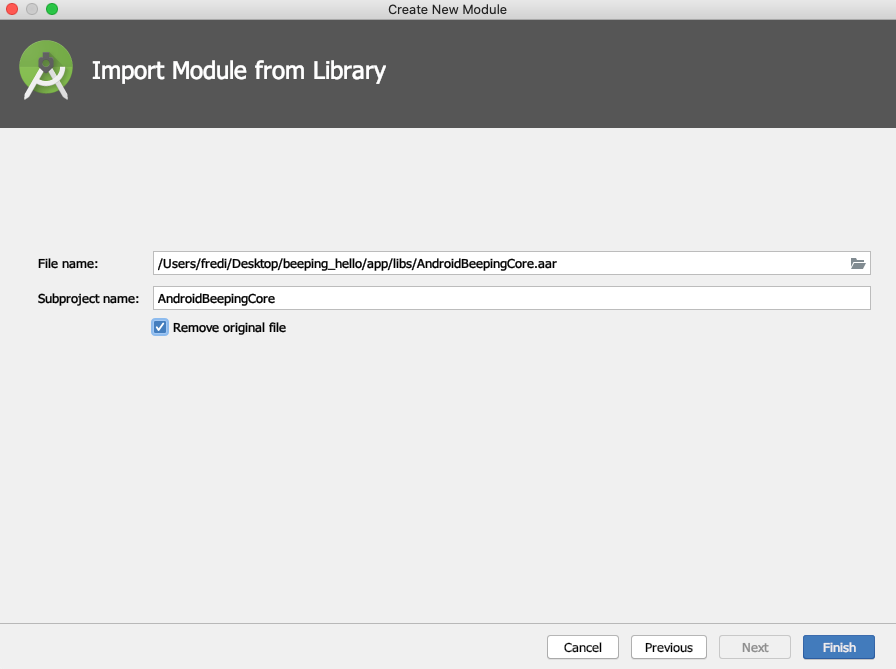
- We copy the framework into the following directory of our app:
$ cp AndroidBeepingCore-release.aar [APP]/AndroidBeepingCore/AndroidBeepingCore.aar
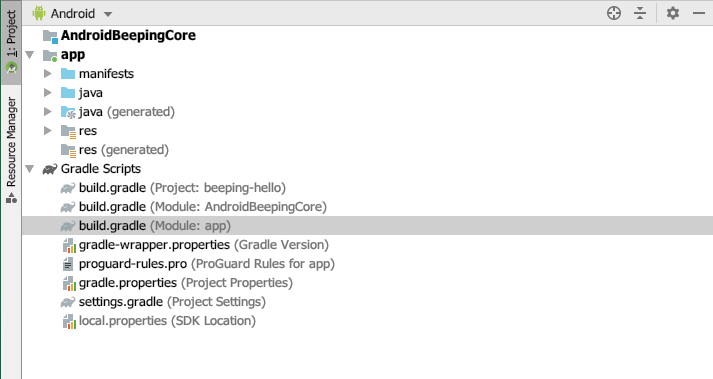
AndroidBeepingCore
When executing the copy command what we have done is to rename the framework. Within our App the framework should be called AndroidBeepingCore.arr
- We import the framework into our project:
- Open the file build.gradle (Module: app)
- Modify the minSdkVersion to version 26:
defaultConfig { applicationId "io.beeping.beeping_hello" minSdkVersion 26 targetSdkVersion 28 versionCode 1 versionName "1.0" testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" }
-
Connect an Android device via USB
-
Select the device in Android Studio and launch the application.
If the app opens correctly, the Beeping Framework will be installed correctly.
Implement the SDK¶
The code we must write to implement the Beeping protocol is very simple.
Here are the steps to implement the source code in your app.
- Open the AndroidManifest.xml file and add the following lines:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="io.beeping.beeping_hello"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO"></uses-permission> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"></uses-permission> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
- Open the file MainActivity.java and add the headers:
package io.beeping.beeping_hello; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCore; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreEvent; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreJNI; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } }
- We added the implementation of Beeping
package io.beeping.beeping_hello; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCore; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreEvent; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreJNI; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements BeepingCoreEvent { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public void beepIdWith(String beepId) { System.out.println("The BeepId is:" + beepId); } }
Callback
When the SDK detects a beep the beepIdWith function will be automatically called, and will receive as parameter the content of the beep. When this happens in our App, what we do is show the content of the beep on our console.
- Beeping Object Declaration
package io.beeping.beeping_hello; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCore; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreEvent; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreJNI; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements BeepingCoreEvent { BeepingCore beeping; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public void beepIdWith(String beepId) { System.out.println("The BeepId is:" + beepId); } }
- The Beeping object is initialized and we tell it to listen
package io.beeping.beeping_hello; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCore; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreEvent; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreJNI; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements BeepingCoreEvent { BeepingCore beeping; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Init Beeping Framework beeping = new BeepingCore(this); // Listening beeping.startBeepingListen(); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public void beepIdWith(String beepId) { System.out.println("The BeepId is:" + beepId); } }
Microphone
In order to listen to the ultrasound and decode its content, the SDK needs access to the microphone to hear what we are sending.
- We tell Beeping to stop listening, once we have read the content of the beep
package io.beeping.beeping_hello; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCore; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreEvent; import com.beeping.AndroidBeepingCore.BeepingCoreJNI; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements BeepingCoreEvent { BeepingCore beeping; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Init Beeping Framework beeping = new BeepingCore(this); // Listening beeping.startBeepingListen(); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public void beepIdWith(String beepId) { System.out.println("The BeepId is:" + beepId); // Stop listening beeping.stopBeepingListen(); } }
The magic¶
What we are going to do now is test our application.
To test our application we must have two elements at hand:
-
Our ultrasound.wav file that is our beep that contains the value qa020
-
The application we just created
We proceed to follow the following steps:
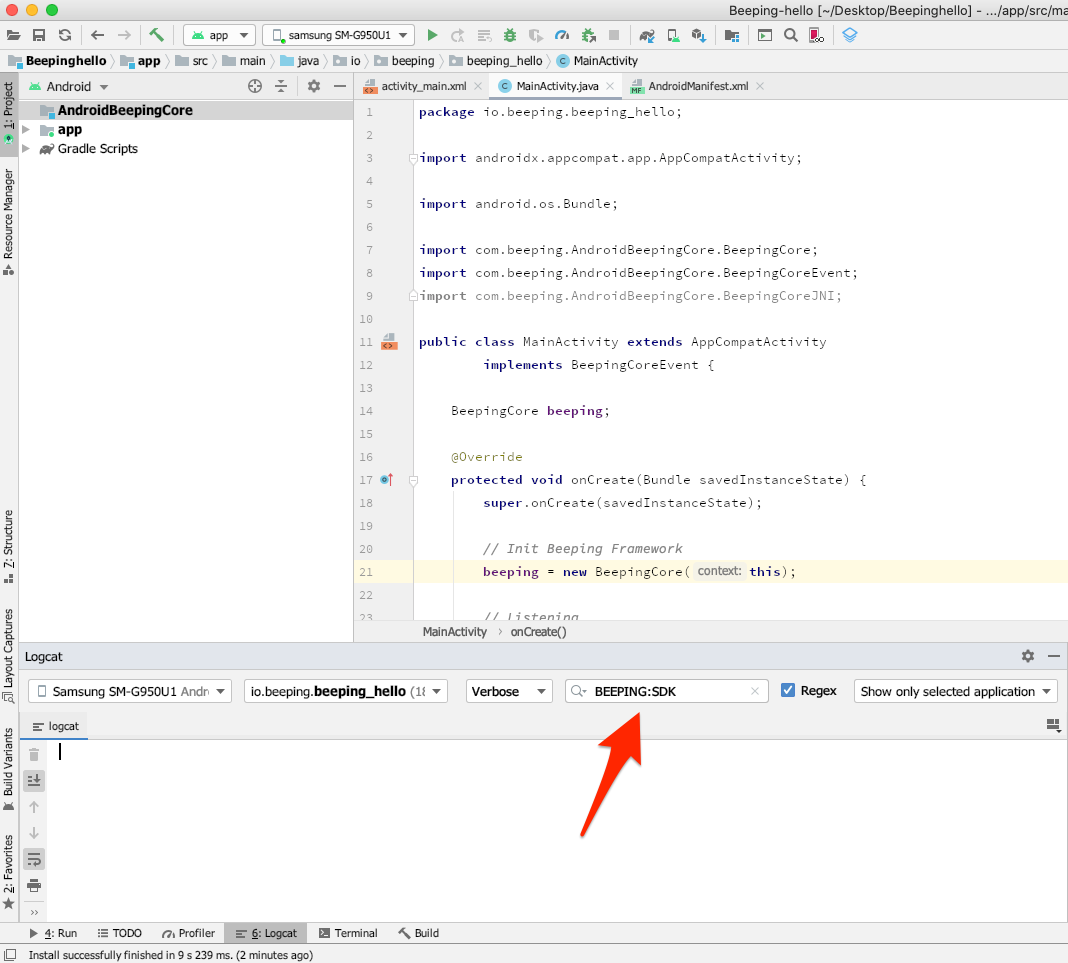
- We open the Logcat of Android Studio
- We select our Android device
- We added a filter to Logcat to see only Beeping text outputs and its SDK
- We start our Android application on our device
If we look at our console we will see the following lines that indicate that beeping is in listening mode:
2020-03-11 16:37:59.676 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: CORE 2020-03-11 16:37:59.677 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: AUDIO-MANAGER 2020-03-11 16:37:59.682 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: ALLOC 2020-03-11 16:37:59.684 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: CONFIGURE 2020-03-11 16:38:00.190 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: LISTENING 2020-03-11 16:38:00.353 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: AUDIOFOCUS_LOSS_TRANSIENT_CAN_DUCK
Now we play our beep and the magic becomes reality.
Notice what has happened on our console:
2020-03-11 16:38:23.505 8559-8591/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: BeepingCallback 2020-03-11 16:38:25.404 8559-8591/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: BeepingCallback 2020-03-11 16:38:25.405 8559-8591/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: BC_TOKEN_END 2020-03-11 16:38:25.406 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello I/System.out: BEEPING:SDK: The BeepId is:qa020 2020-03-11 16:38:25.406 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: DEALLOC 2020-03-11 16:38:25.656 8559-8559/io.beeping.beeping_hello D/BEEPING:SDK: stopBeepingListen
If you look closely at the console, the first lines inform us that Beeping has detected a ulltrasonido, with information.
In the third line we are told that the beep format is correct, and the following lines what they do is read the content and decrypt the information.
Once the process is finished, we are informed that the decryption has worked correctly and internally what the SDK does is to call the function that we have created and that therefore receives the callback.
What it does is write this function in our console in the content of the beep that we have sent you. In our case the following Information: qa020.
Once we have shown the information through the console, what we have done is stop listening to our app and that is what our log shows us in the last line.
API¶
Below we show you the API of the Beeping framework for Android:
Object¶
| Name | Object | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Beeping | BeepingCore | BeepingCore |
Methods¶
| Object | Method | Return | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BeepingCore | new (Context) | instance | Object creation |
| BeepingCore | startBeepingListen() | void | Ready to listen beeps |
| BeepingCore | stopBeepingListen() | void | Stop listening beeps |
Protocol¶
| Object | Type | Callback | Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| BeepingCore | beepingDelegate | beepIdWith:(String beepId) | void |
Links¶
Here you have a series of links related to Android SDK:
Quote¶
Theodore Roosevelt
Do what you can, with what you have, where you are.